Hồng Bàng period
Version française
Vietnamese version
The Vietnamese often say: drinking water reminds us of its source (Uống nước nhớ nguồn). It is not surprising to see them continue to celebrate in great pomp on the 10th day of the third lunar month each year the commemorative day of the Hùng kings of the Hồng Bàng dynasty, the founding fathers of the Vietnamese nation. To this day, no archaeological remains have been found to confirm the existence of this dynasty except for the ruins of the Cổ Loa citadel (Shell City) dating from the reign of King An Dương Vương, the temple built in honor of these Hùng kings in Phong Châu, as well as the jade blades (Nha chương) in Phú Thọ province.
Many clues do not disprove this existence if one refers to the legends reported from this mythical era and the Annals of Vietnam and China. Chinese domination (3rd century BC – 939 AD) was not unrelated to the greatest influence on the development of Vietnamese civilization. Everything belonging to the Vietnamese became Chinese and vice versa during this period. There was a policy of assimilation deliberately imposed by the Chinese. This did not leave the Vietnamese the possibility to maintain their culture, inheriting a civilization 5,000 years old called the « Văn Lang civilization, » without resorting to oral traditions (proverbs, folk poems, or legends).
The use of mythical allusion is the surest way to allow posterity to trace its origin by providing a large number of useful clues despite the systematic destruction of their culture and the relentless repression by the Chinese against the Yue (or the Vietnamese). According to researcher Paul Pozner, Vietnamese historiography is based on a very long and continuous historical tradition. This is represented by an oral historical tradition lasting several centuries of the first millennium BCE in the form of historical legends in the temples of ancestor worship (1).
The two verses found in the following popular song (ca dao):
Trăm năm bia đá thì mòn
Ngàn năm bia miệng vẫn còn trơ trơ
With a hundred years, the stone stele continues to deteriorate
With a thousand years, the words of the people continue to remain in force
testify to the practice consciously carried out by the Vietnamese with the aim of preserving what they inherited from the Văn Lang civilization.
This one bears the name of a kingdom bordered at that time to the north by Nam Hải (Nanhai), to the west by the kingdom of Ba Thuc (Tứ Xuyên or Sichuan in French), to the north by the territory of the Ðộng Ðình lake (Hu Nan) (Hồ Nam), and to the south by the kingdom of Hồ Tôn (Champa). This kingdom was located in the Yangtze River basin (Sông Dương Tử) and was under the authority of a Hùng king. He had been elected for his courage and values. He divided his kingdom into districts entrusted to his brothers known as « Lạc hầu » (marquises). His male children held the title of Quan lang and his daughters that of Mỵ nương. His people were known as Lạc Việt. His men had the custom of tattooing their bodies. This « barbaric » practice, often revealed in Chinese annals, was, according to Vietnamese texts, intended to protect men from attacks by water dragons (con thuồng luồng).
This may be the reason why the Chinese often referred to them as Qủi (demons). A loincloth and topknot constituted the usual costume of this people, to which bronze ornaments were added. The Lạc Việt blackened their teeth with lacquer, chewed betel, and manually pounded rice. As farmers, they practiced rice cultivation in flooded fields.
Is the kingdom of Văn Lang a pure invention fueled by the Vietnamese to maintain a myth, or a real kingdom that existed and disappeared in the whirlwinds of history?
According to Vietnamese myth, the land of these Proto-Vietnamians was bounded to the north during the time of the Hùng Vương (the first dynasty of the Vietnamese, 2879 BC) by Dongting Lake (Động Đình Hồ), located in the territory of the Chu kingdom (Sở Quốc). Part of their territory returned to the latter during the Warring States period (thời Chiến Quốc). Their descendants living in this attached part probably became subjects of the Chu kingdom. There was obviously a relationship, an intimate link between this kingdom and the Proto-Vietnamians. This is a hypothesis recently suggested and advanced by a Vietnamese writer, Nguyên Nguyên(2). According to him, it is not uncommon in ancient texts for ideograms to be replaced by other ideograms with the same phonetics. This is the case with the title Kinh Dương Vương taken by the father of the ancestor of the Vietnamese, Lôc Tục. Writing it this way ![]() in Chinese, one can easily see the names of two cities: Kinh Châu (Jīngzhōu)(3) and Dương Châu (Yángzhōu)(4), where respectively the Yue ethnic groups of the Thai branch and the Lạc branch lived. There was a translation of an intention to intelligently evoke by the narrator the settlement and fusion of the Yue ethnic groups of the Thai branch (Si Ngeou) and the Lạc branch (Ngeou-lo) coming from migrations from these cities during the conquests and annexations of Chu. On the other hand, the ideogram 陽 (thái dương) is translated as light, solemn.
in Chinese, one can easily see the names of two cities: Kinh Châu (Jīngzhōu)(3) and Dương Châu (Yángzhōu)(4), where respectively the Yue ethnic groups of the Thai branch and the Lạc branch lived. There was a translation of an intention to intelligently evoke by the narrator the settlement and fusion of the Yue ethnic groups of the Thai branch (Si Ngeou) and the Lạc branch (Ngeou-lo) coming from migrations from these cities during the conquests and annexations of Chu. On the other hand, the ideogram 陽 (thái dương) is translated as light, solemn.
It is used in order to avoid its use as a family name. By using these words, it allows the translation of Kinh Dương Vương as the solemn King Kinh. But there is also a word Kinh 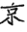 synonymous with the word Lac (
synonymous with the word Lac (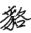 ), a nickname for the Viet. In short, Kinh Dương Vương
), a nickname for the Viet. In short, Kinh Dương Vương ![]() can be translated as the Solemn Viet King. As for the title An Dương Vương taken by the king of Âu Viêt, the author does not doubt his explanation: it is indeed the pacification of the Yue country of the Lac branch (trị an xứ Dương) by a son of the Yue of the Thái branch.
can be translated as the Solemn Viet King. As for the title An Dương Vương taken by the king of Âu Viêt, the author does not doubt his explanation: it is indeed the pacification of the Yue country of the Lac branch (trị an xứ Dương) by a son of the Yue of the Thái branch.
This can only support the thesis of Edouard Chavannes (5) and Léonard Aurousseau (5): the Proto-Vietnamese and the subjects of the Chu kingdom have the same ancestors. Moreover, there is a remarkable coincidence found in the clan name Mị (咩) (the bleating of a sheep) borne by the kings of Chu and that of the Vietnamese kings. Based on the Historical Memoirs (Che-Ki) of Sseu-Ma Tsien (Sima Qian) translated by E. Chavannes (6), it is known that the king of the Chu principality comes from the southern barbarians (or Bai Yue): Hiong-K’iu (Hùng Cừ) said: I am a barbarian and I do not take part in the posthumous titles and names of the kingdoms of the Middle.
American linguists Mei Tsulin (6) and Norman Jerry have identified a number of loanwords from the Austro-Asiatic language of the Yue in Chinese texts from the Han period.
This is the case with the Chinese word jiang 囝 (giang in Vietnamese or river in French) or the word nu (ná in Vietnamese or crossbow in French). They demonstrated the strong probability of the presence of the Austro-Asiatic language in southern China and concluded that there had been contact between the Chinese language and the Austro-Asiatic language in the territory of the ancient kingdom of Chu between 1000 and 500 years before Christ. This geographical argument was never seriously considered in the past by some Vietnamese historians because, for them, this dynasty belonged rather to the mythical period. Moreover, according to Chinese sources, the territory of the ancestors of the Vietnamese (Kiao-tche (Giao Chỉ) and Kieou-tchen (Cửu Chân)) was confined to present-day Tonkin, which made them reluctant to accept without explanation or justification the territorial extent of the Hồng Bàng dynasty up to Dongting Lake. They did not see in the narration of this myth the will of the ancestors of the Vietnamese to show their origin, to display their belonging to the Bai Yue group, and their unwavering resistance against the formidable conquerors who were the Chinese.

In the Chinese annals, it was reported that during the Spring and Autumn period (Xuân Thu), King Gou Jian (Câu Tiễn) of the Yue (Wu Yue) was interested in an alliance he wished to form with the kingdom of Văn Lang in order to maintain supremacy over the other powerful principalities in the region. It is likely that this kingdom of Văn Lang was a neighboring country to that of Gou Jian’s Yue.
He found no interest in forming this alliance if the Văn Lang kingdom was geographically confined to present-day Vietnam. The recent discovery of King Goujian of Yue’s sword (reigned 496-465 BC) in tomb no. 1 of Wanshan (Jianling) (Hubei) helps to better define the boundaries of the Văn Lang kingdom. It would probably be located in the Qui Châu (or GuiZhou) region. However, Henri Maspero challenged this hypothesis in his work titled « The Kingdom of Văn Lang » (BEFEO, vol. XVIII, no. 3).
He attributed to Vietnamese historians the error of confusing the Văn Lang kingdom with that of Ye Lang (or Dạ Lang in Vietnamese), whose name may have been incorrectly transmitted by Chinese historians to their Vietnamese colleagues during the Tang dynasty (nhà Đường). This is not entirely accurate because, in Vietnamese legends, particularly in that of « Phù Ðổng Thiên Vương (or the Celestial Lord of Phù Ðổng village), » it is evident that the Văn Lang kingdom was in armed conflict with the Yin-Shang (Ân-Thương) dynasty during the reign of King Hùng VI and that it was larger than the Ye Lang kingdom found at the time of China’s unification by Qin Shi Huang Di.

In the Annals of Viet Nam, the long reign of the Hùng kings (from 2879 to 258 BC) is mentioned. The discovery of bronze objects in Ningxiang (Hu Nan) in the 1960s eliminated any doubt about the existence of centers of civilization contemporary with the Shang, which were ignored by texts in southern China. This is the case, for example, with the Sanxingdui culture (Sichuan) (Di chỉ Tam Tinh Đôi). The bronze wine vessel decorated with anthropomorphic faces clearly testifies to contact established by the Shang with Melanesian-type peoples, as these faces show round human faces with a flat nose. The casting of this bronze used in the making of this vessel requires the incorporation of tin, which northern China did not possess at that time.
Could there have been real contact, an armed conflict between the Shang and the kingdom of Văn Lang if we stick to the legend of the celestial lord of Phù Ðổng? Could we grant truthfulness to a fact reported by a Vietnamese legend? Many Western historians have always seen the Đông Sơn civilization period as the beginning of the formation of the Vietnamese nation (500-700 BC). This is also the shared opinion found in the anonymous historical work « Việt Sử Lược. »
Under the reign of King Zhuang Wang (Trang Vương) of the Zhou (696-691 BC), there was in the Gia Ninh district a strange figure who succeeded in dominating all the tribes with his magic, taking the title Hùng Vương and establishing his capital at Phong Châu. Through hereditary succession, this allowed his lineage to maintain power with 18 kings, all bearing the name Hùng.
On the other hand, in other Vietnamese historical works, a long period of reign was attributed to the Hồng Bàng dynasty (from 2879 to 258 BC) lasting 2622 years. It seems inconceivable if we stick to the number 18, the number of kings during this period, because that would mean each Hùng Vương king reigned on average 150 years. We can only find a satisfactory answer if we accept the hypothesis established by Trần Huy Bá in his presentation published in the journal Nguồn Sáng no 23 on the day of commemoration of the Hùng Vương kings (Ngày giỗ Tổ Hùng Vương) (1998). For him, there is a misinterpretation of the word đời found in the phrase « 18 đời Hùng Vương. » The word « Ðời » should be replaced by the word Thời meaning « period. » (7)

With this hypothesis, there are therefore 18 reign periods, each corresponding to a branch that can be composed of one or several kings in the genealogical tree of the Hồng Bàng dynasty. This argument is reinforced by the fact that King Hùng Vương was elected for his courage and merits, referring to the Vietnamese tradition of choosing men of value for the supreme position. This was reported in the famous legend of the sticky rice cake (Bánh chưng bánh dầy). Thus, the word đời can be justified by the word branch (or chi).
We are led to provide a more coherent explanation for the number 2622 with the following 18 branches found in the work « Văn hoá tâm linh – đất tổ Hùng Vương » by the author Hồng Tử Uyên:
| Chi Càn | Kinh Dương Vương húy Lộc Túc |
| Chi Khảm | Lạc Long Quân húy Sùng Lãm |
| Chi Cấn | Hùng Quốc Vương húy Hùng Lân |
| Chi Chấn | Hùng Hoa Vương húy Bửu Lang |
| Chi Tốn | Hùng Hy Vương húy Bảo Lang |
| Chi Ly | Hùng Hồn Vương húy Long Tiên Lang |
| Chi Khôn | Hùng Chiêu Vương húy Quốc Lang |
| Chi Ðoài | Hùng Vĩ Vương húy Vân Lang |
| Chi Giáp | Hùng Ðịnh Vương húy Chân Nhân Lang |
| ………….. | manquant dans le document historique … |
| Chi Bính | Hùng Trinh Vương húy Hưng Ðức Lang |
| Chi Ðinh | Hùng Vũ Vương húy Ðức Hiền Lang |
| Chi Mậu | Hùng Việt Vương húy Tuấn Lang |
| Chi Kỷ | Hùng Anh Vương húy Viên Lang |
| Chi Canh | Hùng Triệu Vương húy Cảnh Chiêu Lang |
| Chi Tân | Hùng Tạo Vương húy Ðức Quân Lang |
| Chi Nhâm | Hùng Nghị Vương húy Bảo Quang Lang |
| Chi Qúy | Hùng Duệ Vương |
This also allows us to trace the storyline in the armed conflict between the kingdom of Văn Lang and the Shang through the legend of « Phù Ðổng Thiên Vương. » If this conflict took place, it could only have been at the beginning of the Shang dynasty’s reign for several reasons:
1) No Chinese or Vietnamese historical document mentions trade relations between the kingdom of Văn Lang and the Shang. However, contact was noted later between the Zhou dynasty and King Hùng Vương. A silver pheasant (chim trĩ trắng) was even offered by the latter to the king of Zhou according to the work Linh Nam Chích Quái.
2) The Shang dynasty only reigned from 1766 to 1122 BC. There would be approximately a 300-year discrepancy if one attempted to calculate the arithmetic mean of 18 reign periods of the Hùng kings: (2622 / 18) and multiply it by 12 to roughly give a date at the end of the reign of the sixth Hùng branch (Hùng Vương VI), adding 258, the year of the annexation of the Văn Lang kingdom by King An Dương Vương. This would bring us roughly to the year 2006, the end of the reign of the sixth Hùng branch (Hùng Vương VI). It can be deduced that if there was a conflict, it should be at the beginning of the advent of the Shang dynasty. This discrepancy is not entirely unjustified since there has been little historical precision so far beyond the reign of King Chu Lệ Vương (Zhou LiWang) (850 BC).

